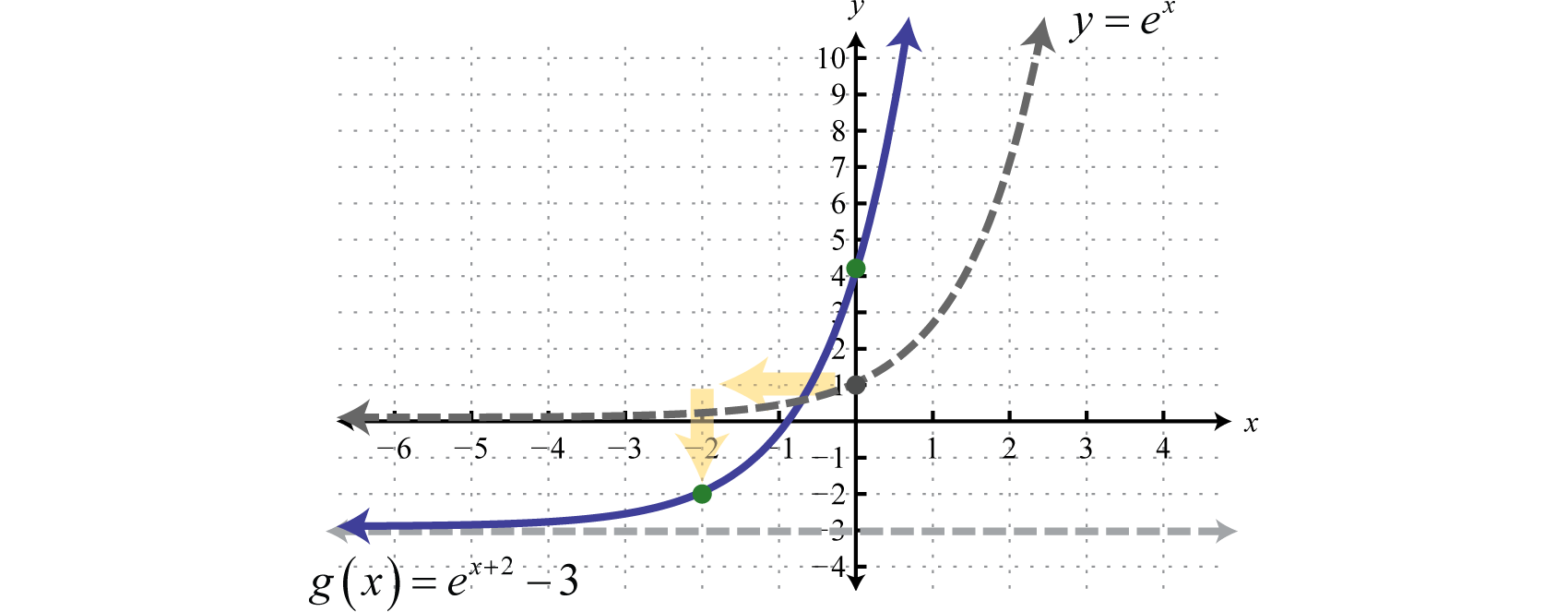
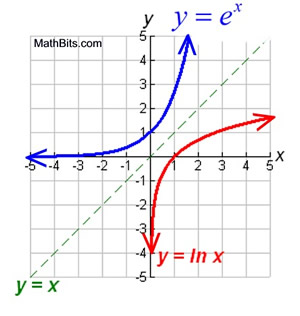
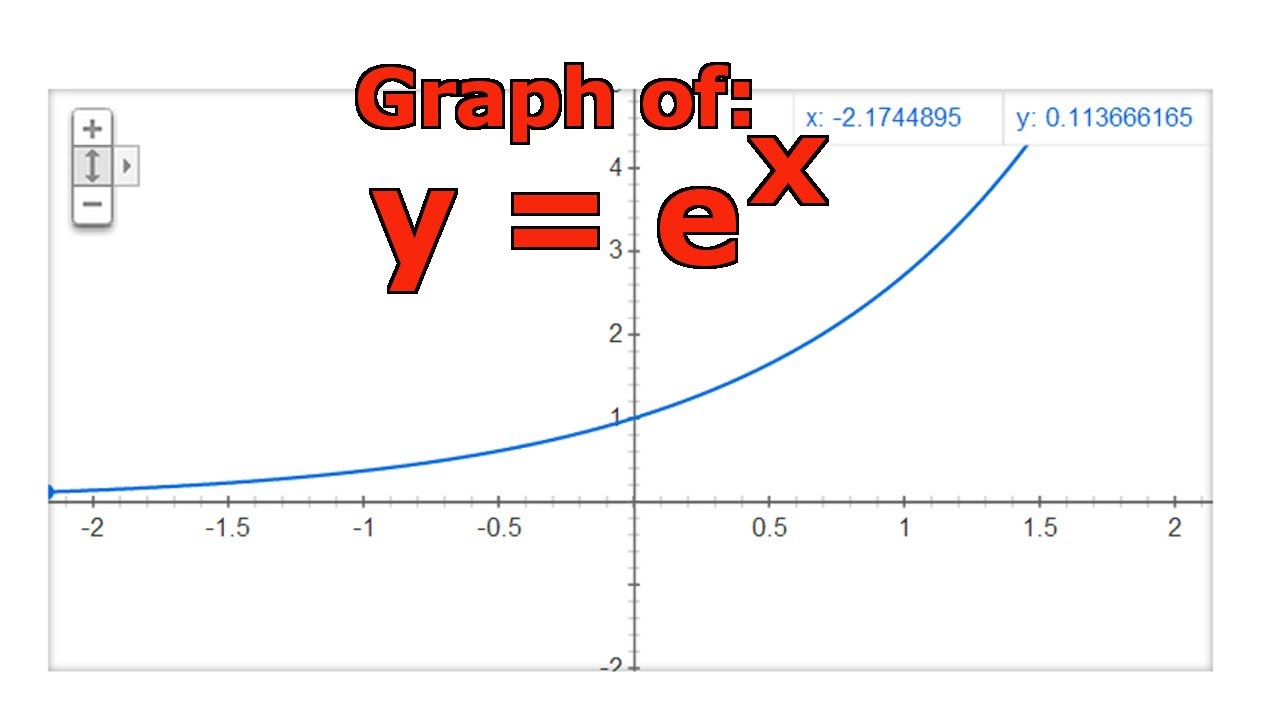
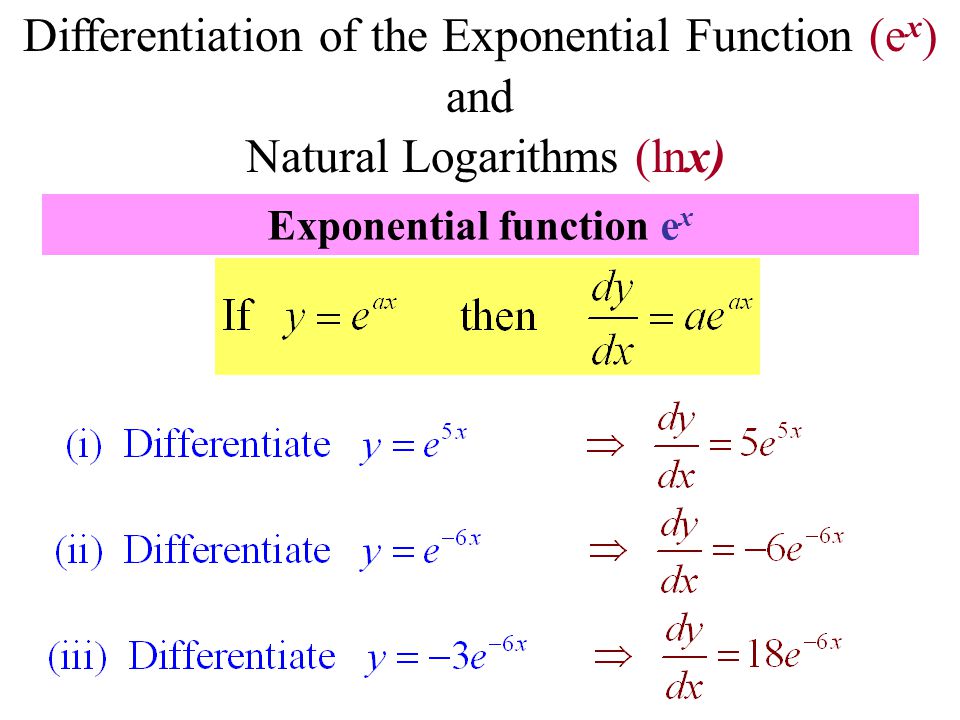
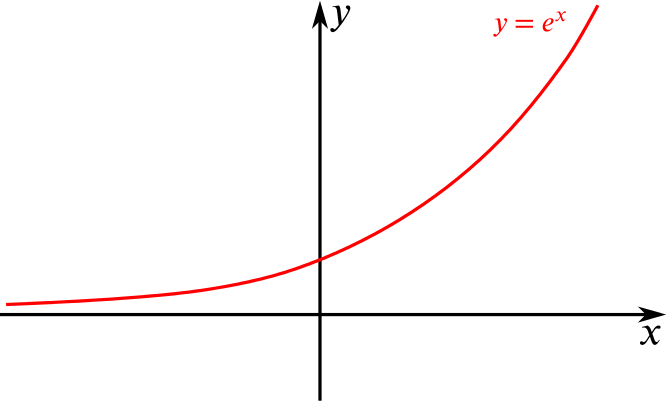
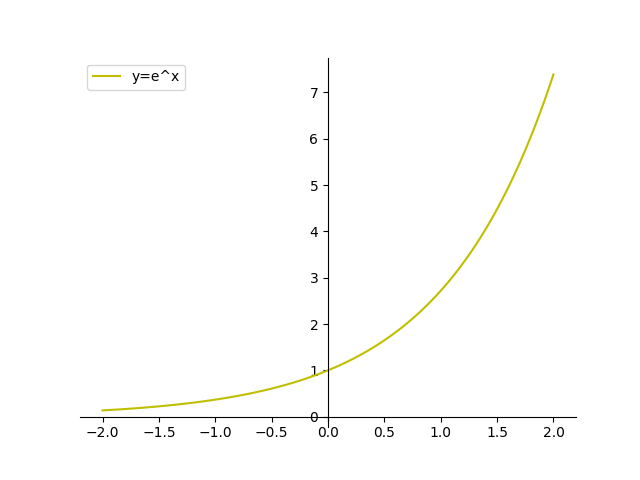
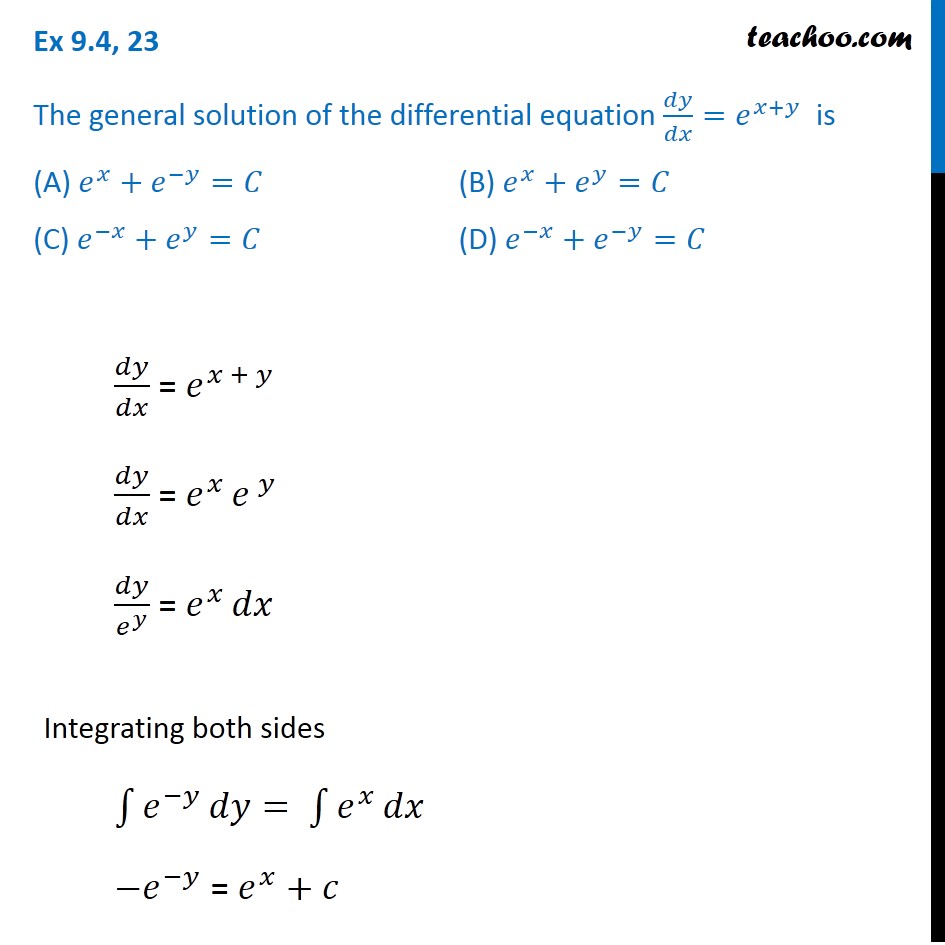
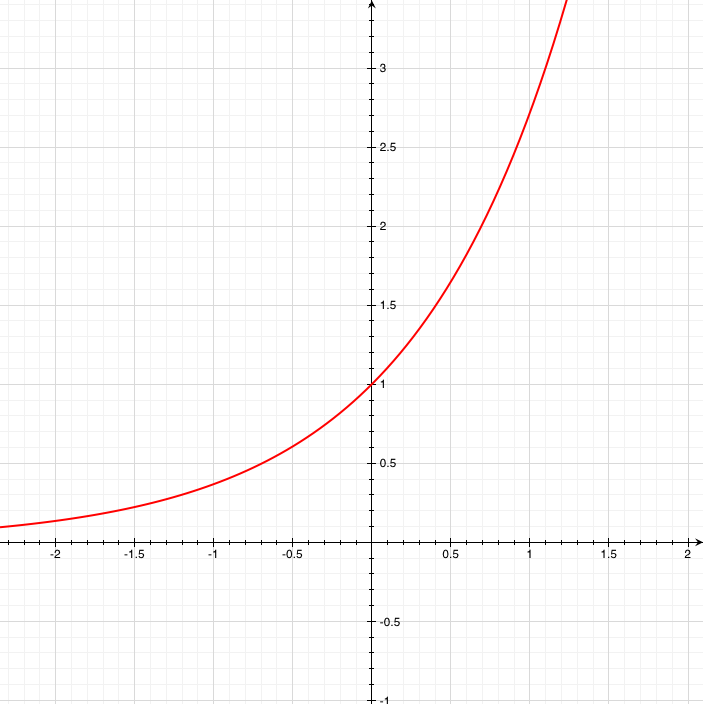
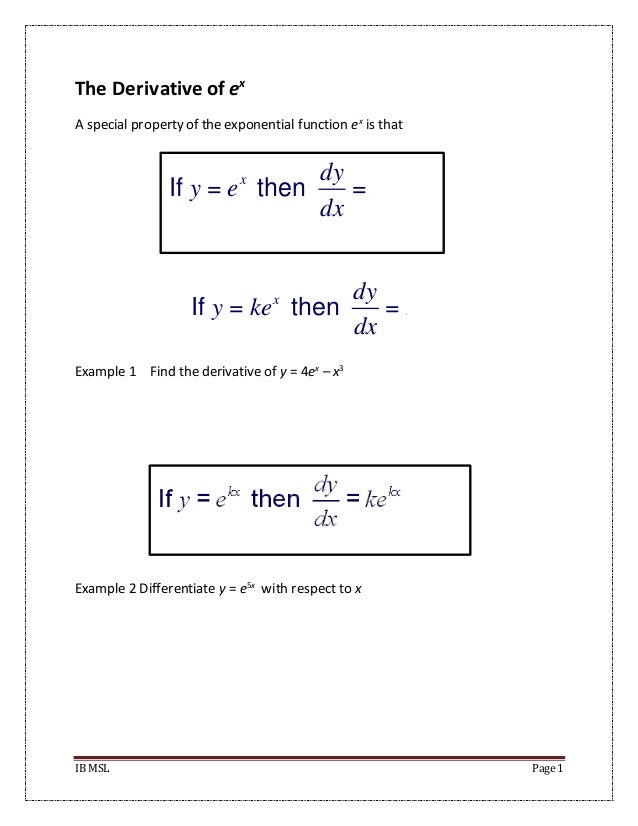
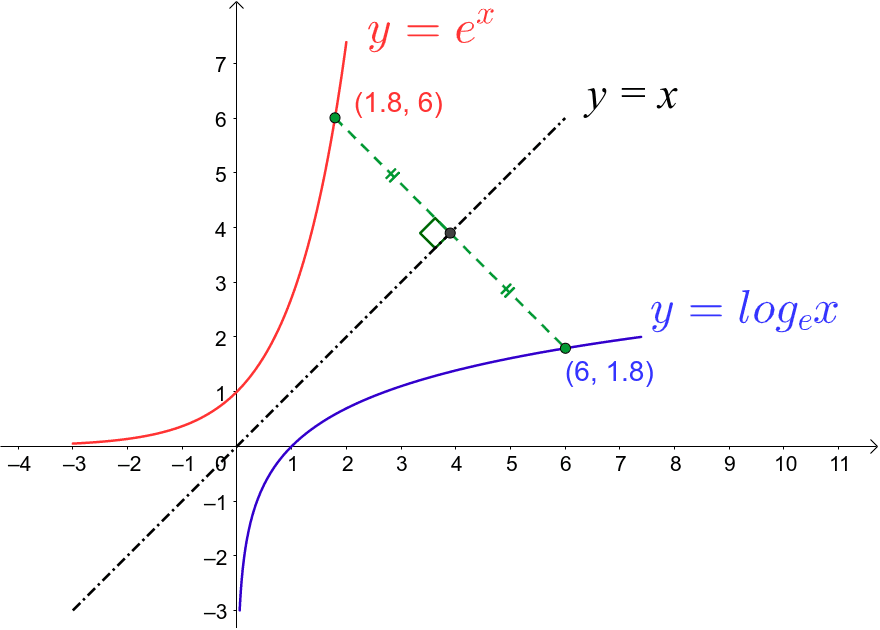
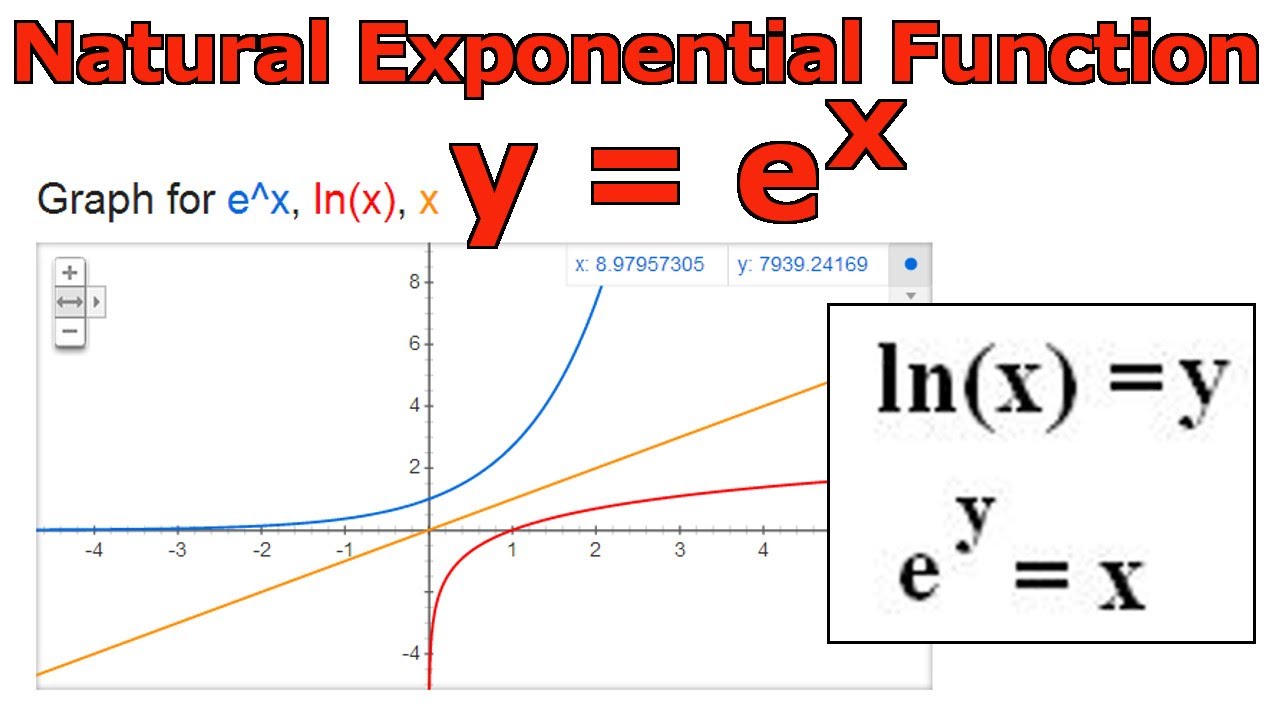
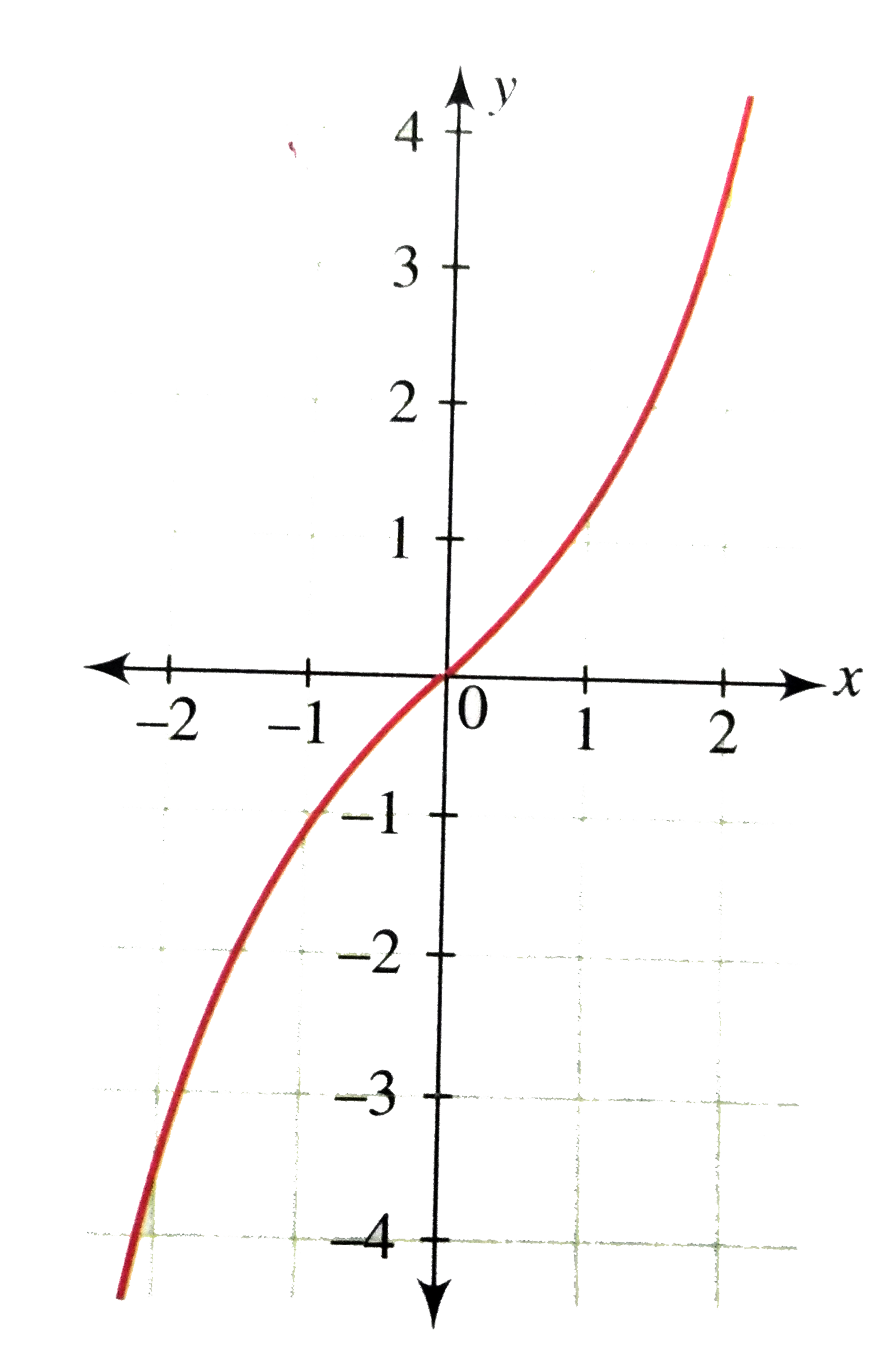
√ y=e^-x 300544-Y e x logarithmic form
G = C 3 e i x So we need to determine what value (if any) of the constant C 3 makes g(x) = f(x) If we set x=0 and evaluate f(x) and g(x), we get f(x) = cos( 0 ) i sin( 0 ) = 1 g(x) = C 3 e i 0 = C 3 These functions are equal when C 3 = 1 Therefore, cos( x ) i sin( x ) = e i x Justification #2 the series method (This is the usual justification given in textbooks) By use of Taylors
Y e x logarithmic form-Have a question about using WolframAlpha?Integrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi;
Y e x logarithmic formのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
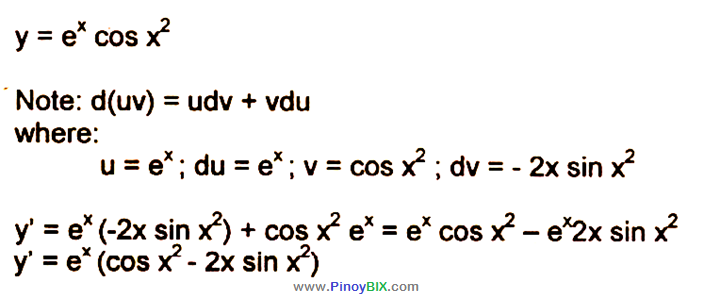 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
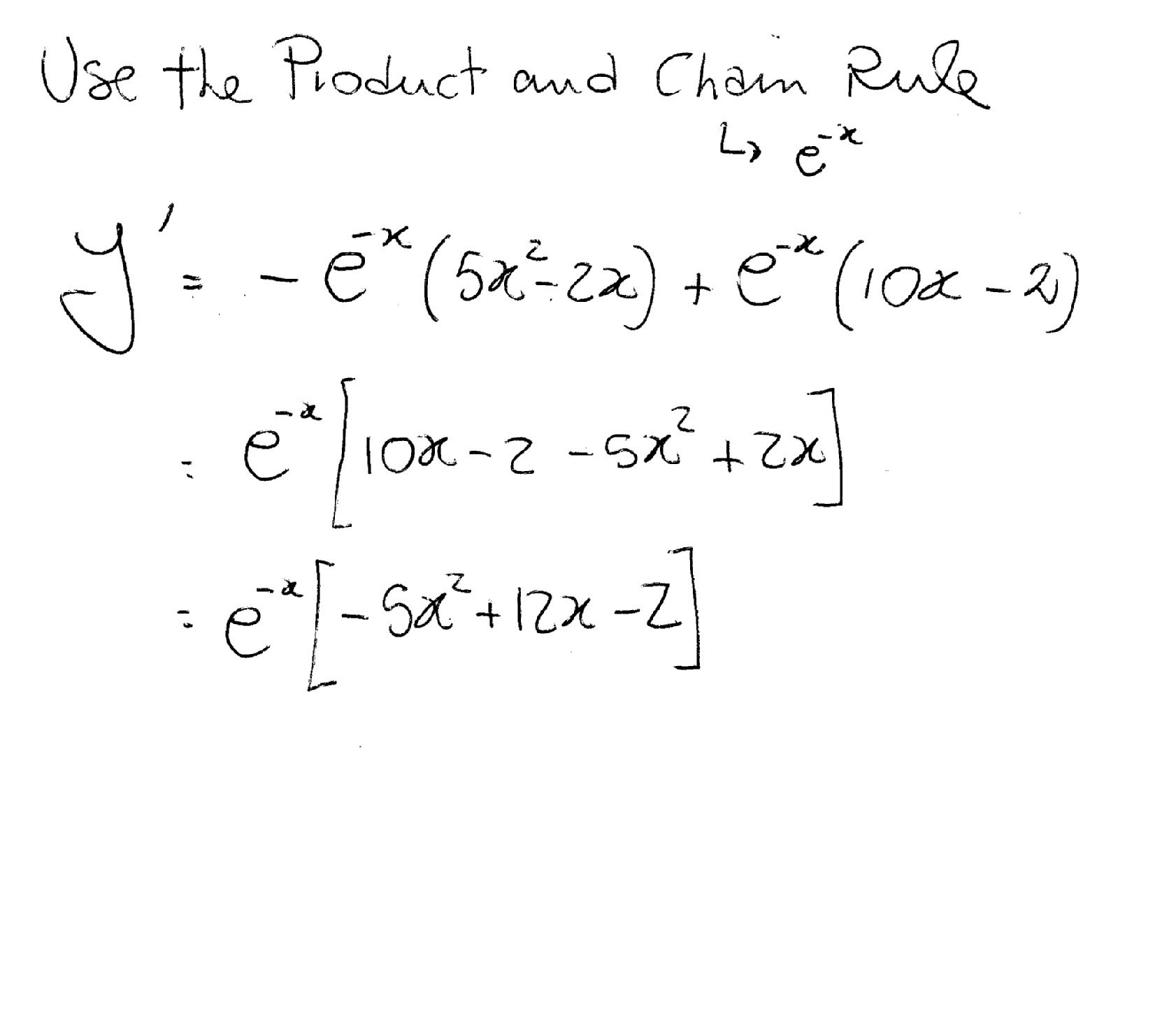 |  | |
 |  |  |
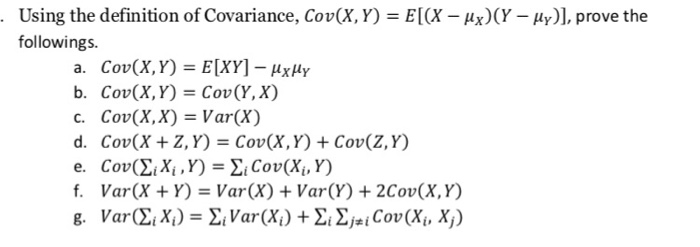 |  | |
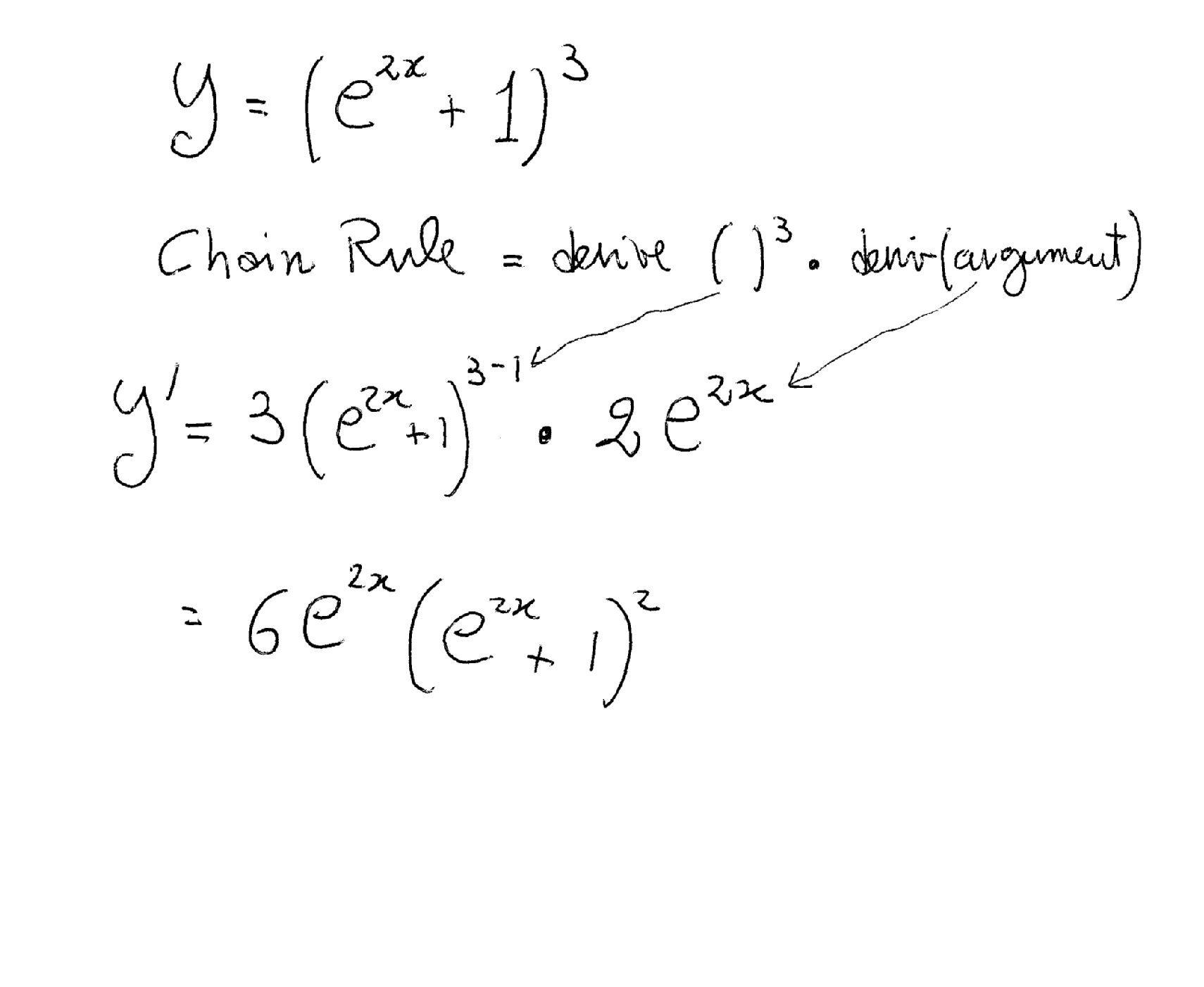 | ||
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 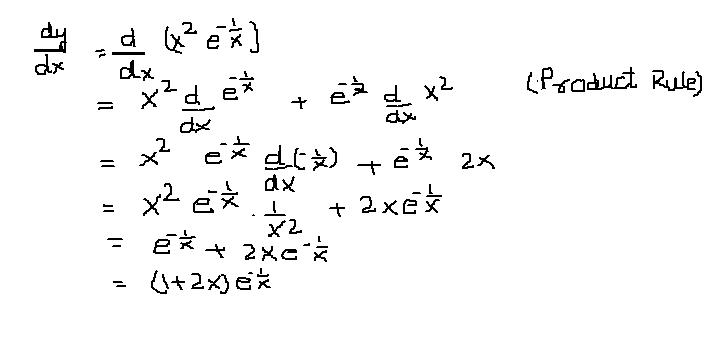 | |
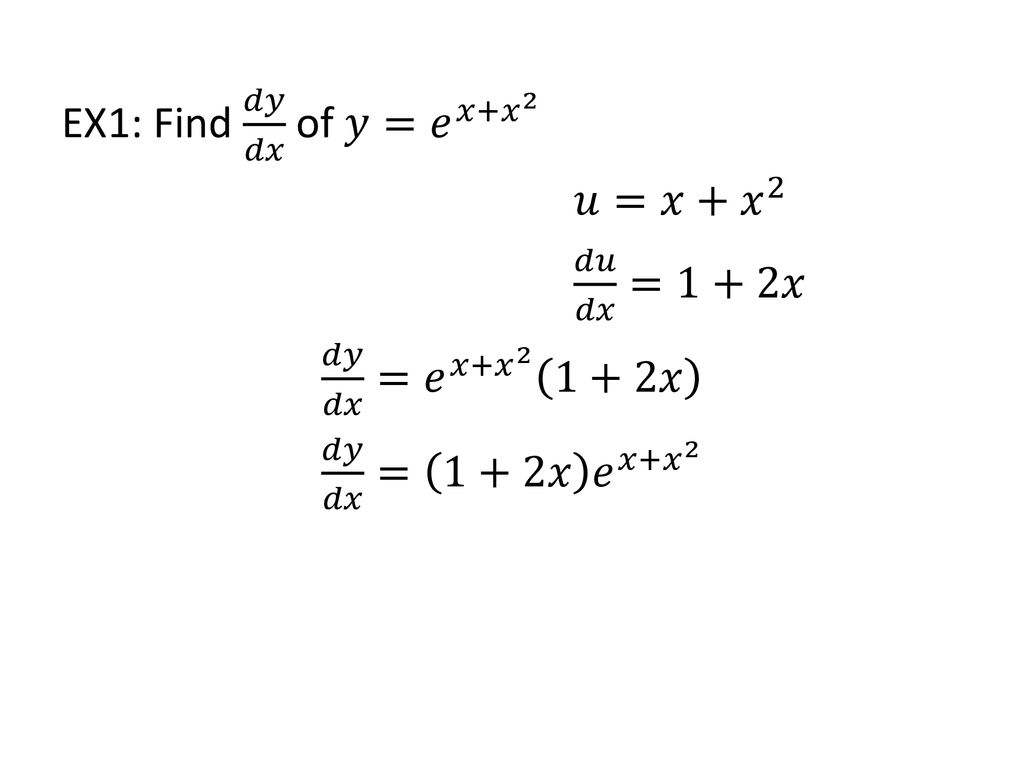 |  | |
 |  | |
 | 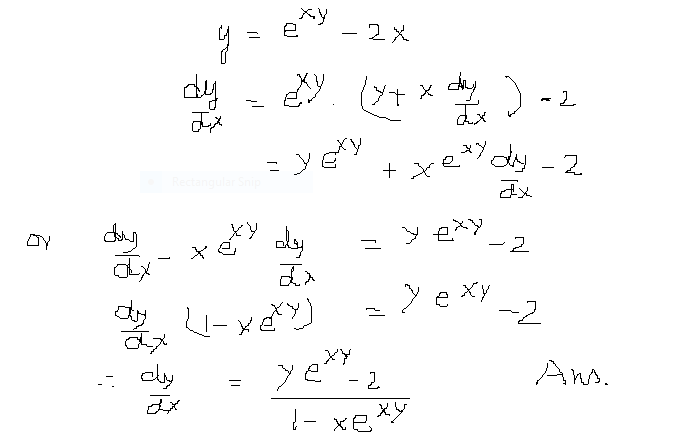 |  |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | 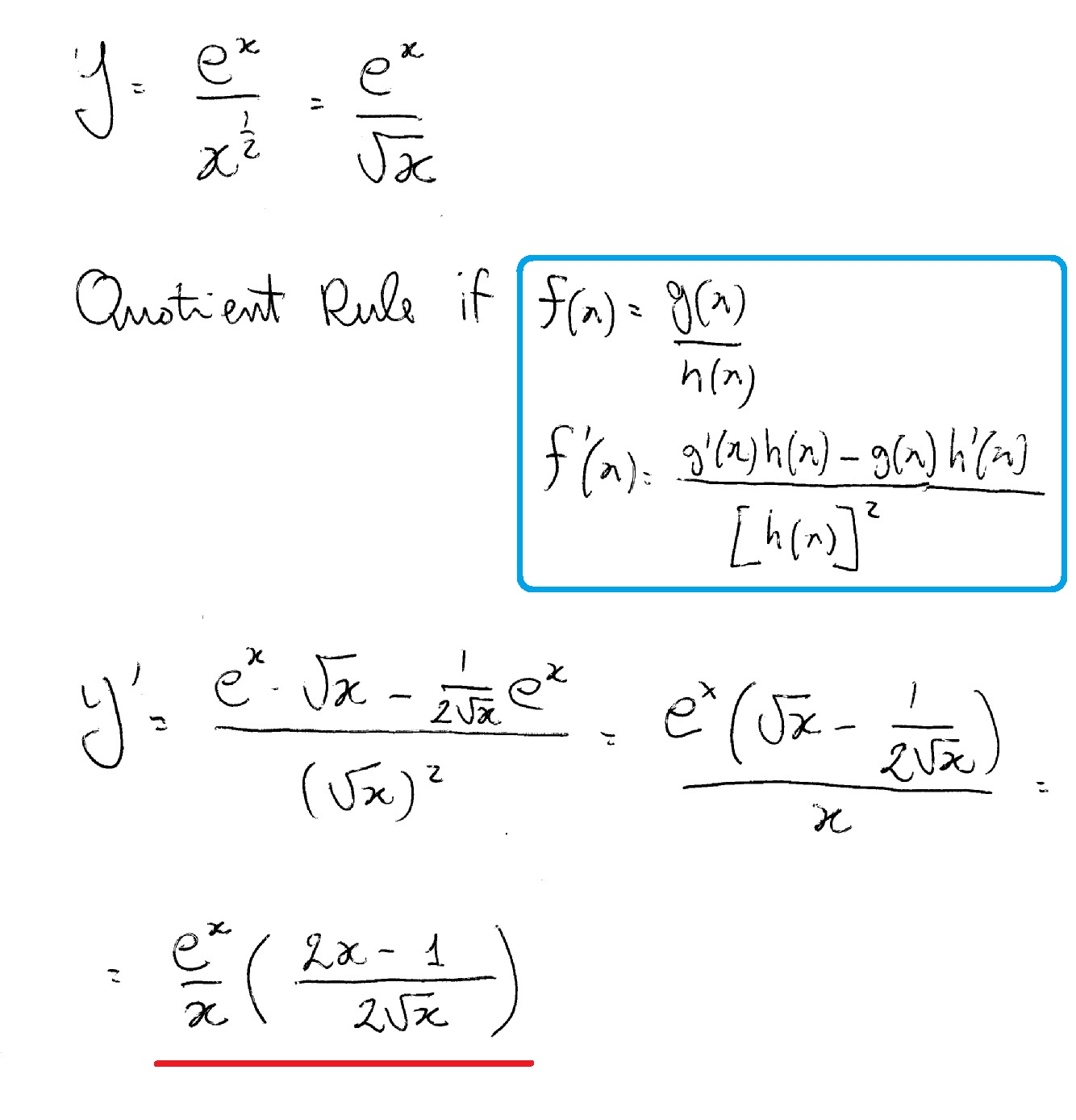 | |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
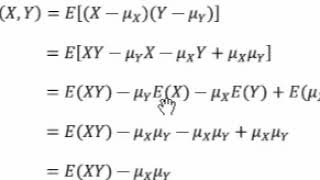 |  |  |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
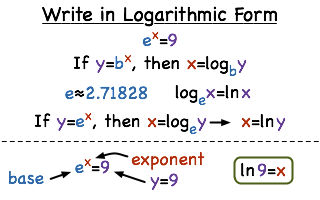 |  | |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y e x logarithmic form」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
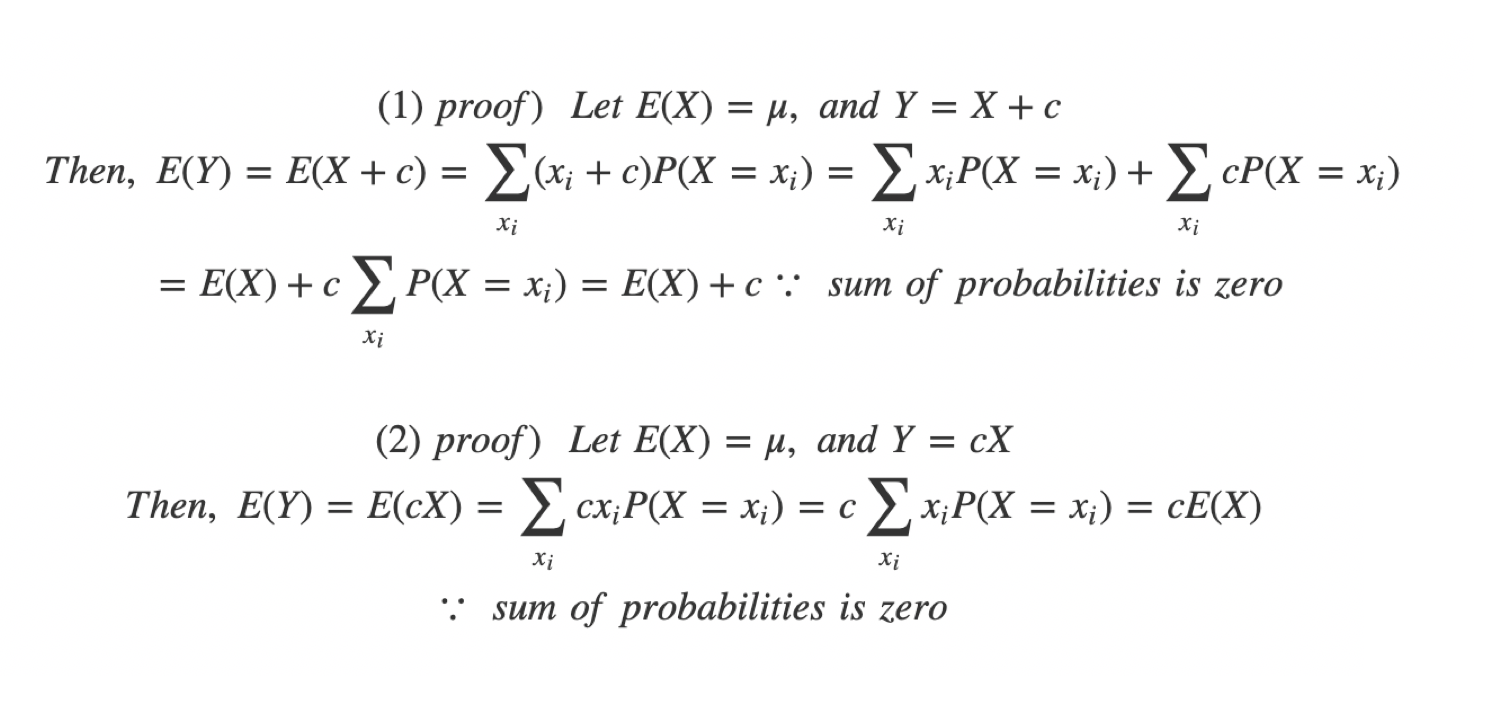 |  | |
 |
= Var(X)Var(Y)2EXY−2EXEY But we've just seen that EXY = EXEY if X and Y are independent, so then Var(X Y) = Var(X)Var(Y) 3 Binomial random variables Recall that the distribution of the binomial is ProbX = x = n x p x(1−p)n− and that it's the sum of n independent Bernoulli variables with parameter p 3 How do we know this is a valid probability distribution?See below, left x y x 1 y 1 y=(1/z)x support set of support set with (x/y)0 Blue subset To find the density, fZ(z), we start, as always, by finding the cdf, FZ(z) = P(Z ≤ z), and then
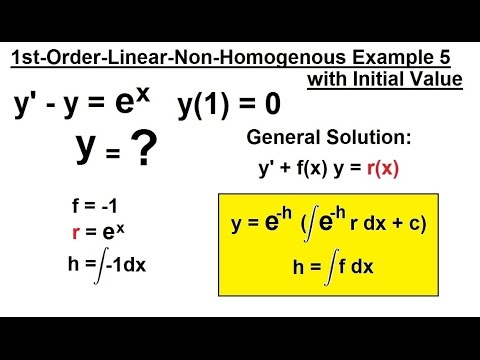
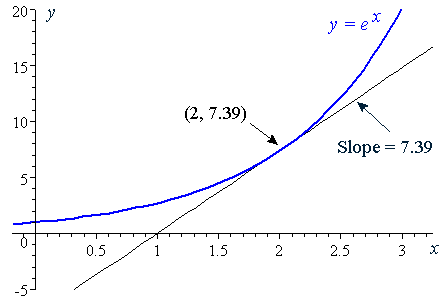
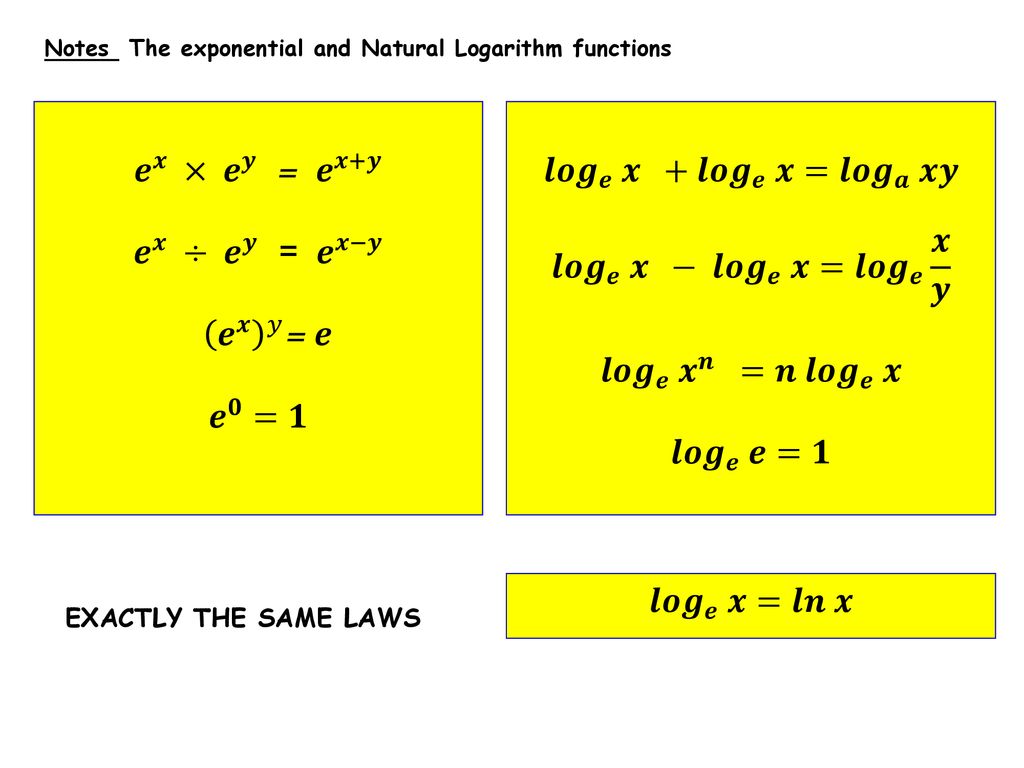
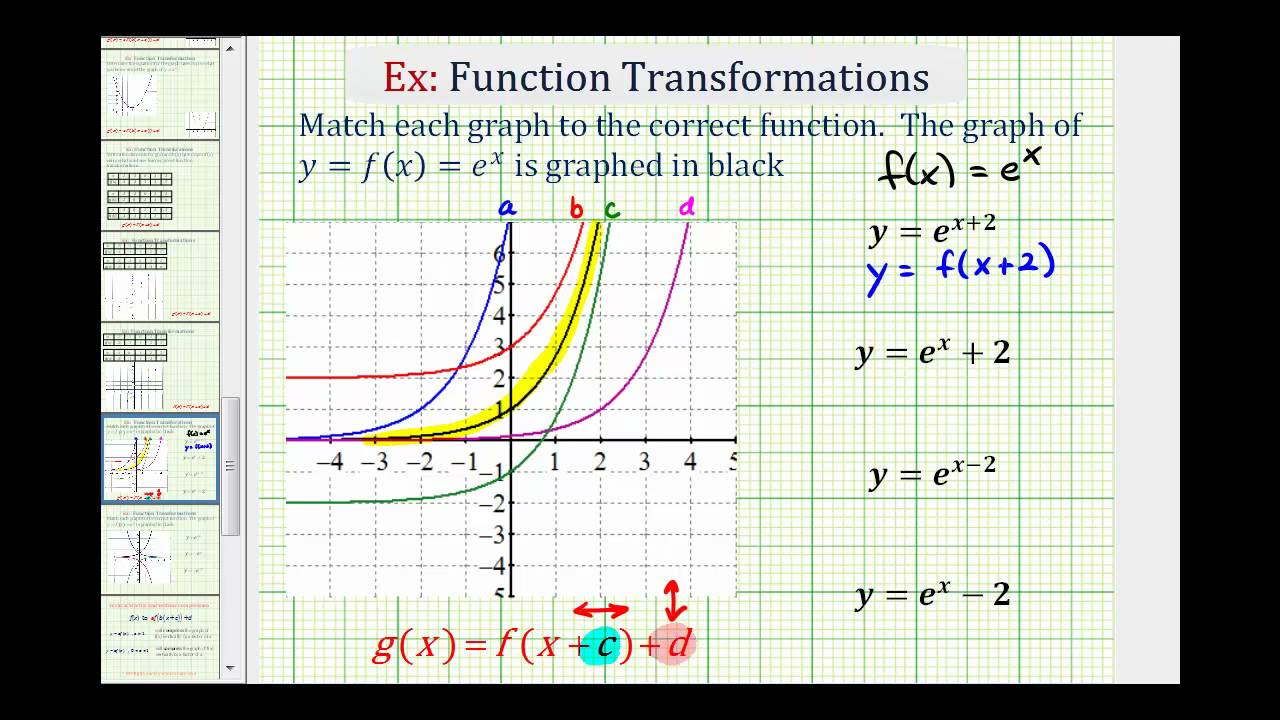
Incoming Term: y e x oriental store, y e x = + differentiation w.r.t. 'x', y e x logarithmic form, y=e^x, y=e^x graph, y=e^x-1, y=e^x(acosx+bsinx), y=e^x(sinx+cosx), y e x do vertice, y=e^x find dy/dx,
コメント
コメントを投稿